Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
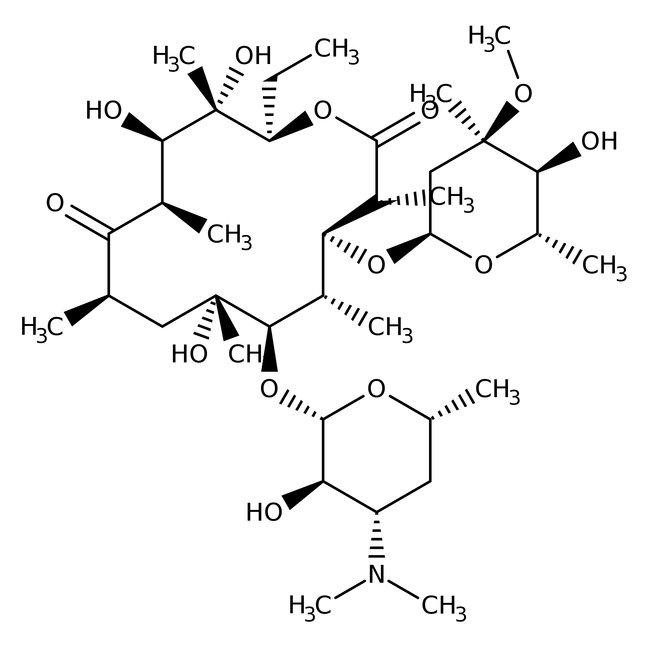
Erythromycin, Cell Culture Grade
Erythromycin (E-Mycin or erythrocin), CAS # 114-07-8, is a broad-spectrum antibiotic. | CAS: 114-07-8 | C37H67NO13 | 733.94 g/mol
| Catalog Number | Quantity |
|---|---|
| ALFJ62279.09 | 10 g |
Catalog number ALFJ62279.09
View Price:Sign InSign in to see your account pricing. Need an account? Register with us today.
Quantity:
10 g
Specifications
Chemical Name or MaterialErythromycin
TypeErythromycin
Physical FormCrystalline Powder
CAS114-07-8
Recommended StorageAmbient temperatures
View more
Erythromycin, is used as a macrolide antibiotic protein synthesis inhibitor. It is widely used in cell culture applications. Depending upon the strain of bacteria, erythromycin has been used between 50 and 200 mg/L to control bacterial growth. Erythromycin resistance can be induced in bacteria.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
General Description
- Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic that works by binding the 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibiting polypeptide formation
- Erythromycin was isolated from Saccharopolyspora erythraea
Applications
- Erythromycin can be used to disrupt the growth of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
- Erythromycin has been shown to have motor effects in the gastrointestinal system and can be used for laboratory research on migrating motor complex activity
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- Dreno, B.; Martin, R.; Moyal, D.; Henley, J.B.; Khammari, A.; Seité, S. Skin microbiome and acne vulgaris: Staphylococcus, a new actor in acne. Exp Dermatol. 2017, 26(9), 798-803.
- Wu, F.; Tokach, M.D.; DeRouchey, J.M.; Dritz, S.S.; Woodworth, J.C.; Goodband, R.D.; Chitakasempornkul, K.; Bello, N.M.; Capps, K.; Remfry, S.; Scott, H.M.; Nagaraja, T.G.; Apley, M.D.; Amachawadi, R.G. Effects of Tylosin Administration Routes on the Prevalence of Antimicrobial Resistance Among Fecal Enterococci of Finishing Swine. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2019, 16(5), 309-316.