Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
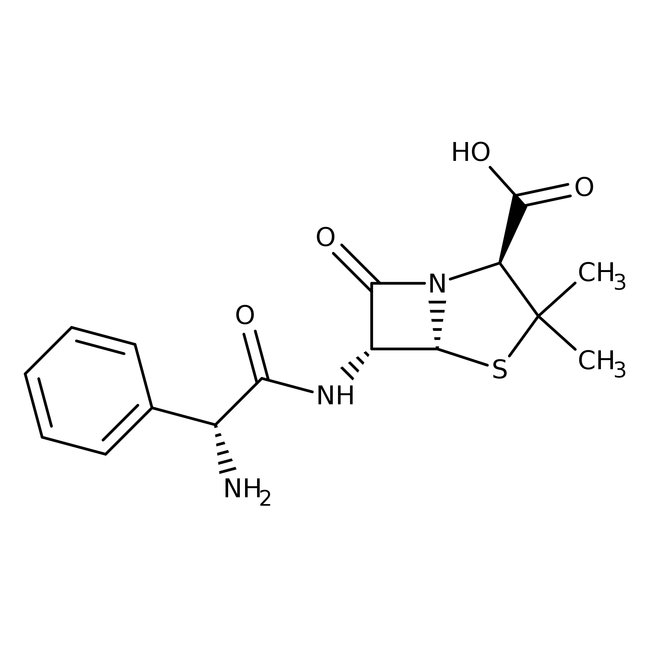
Ampicillin
Ampicillin, CAS # 69-53-4, is structurally related to penicillin and is considered to be a semi-synthetic antibiotic with antibacterial activity. | CAS: 69-53-4 | C16H19N3O4S | 349.405 g/mol
Catalog number ALFJ60977.14
View Price:Sign InSign in to see your account pricing. Need an account? Register with us today.
Quantity:
25 g
Specifications
Chemical Name or MaterialAmpicillin
TypeAmpicillin
Physical FormPowder
CAS69-53-4
Health Hazard 1H315-H317-H319-H334-H335
View more
Ampicillin is used as asemi-synthetic antibiotic which has antibacterial activity structurally related to penicillin. It is widely used selection reagent for transformed cells expressing β-lactamase. It is also used to prevent and treat a number of bacterial infections. It may also be used to prevent group B streptococcal infection in newborns.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
General Description
- Ampicillin is a broad-spectrum, semi-synthetic, β-lactam penicillin with bactericidal activity. It acts against several gram-positive and -negative infections
- This compound binds to and inactivates penicillin-binding proteins (PBP) located on the inner membrane of the bacterial cell wall. This inactivation interferes with the cross-linkage of peptidoglycan chains essential for bacterial cell wall strength and rigidity. Consequently, there is an interruption in the bacterial cell wall synthesis which results in the weakening of the bacterial cell wall causing cell lysis
Application
- In laboratory experiments, it is commonly used as a selector reagent for transformed cells expressing β-lactamase. The ampicillin-resistant gene (ampR) catalyzes the hydrolysis of the β-lactam ring of ampicillin and naturally detoxifies the drug
- Ampicillin is commonly used as a selection marker for E. coli and other bacteria during plasmid DNA isolation, protein expression, and gene cloning
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- Zhao Z., Baldo BA., O'Brien RM., Plomley RF. Reaction with, and fine structural recognition of polyamines by human IgE antibodies. Molecular immunology . 2000, 37,(5), 233-240.
- Harmoinen J., Vaali K., Koski P., Syrjänen K., Laitinen O., Lindevall K., Westermarck E. Enzymic degradation of a beta-lactam antibiotic, ampicillin, in the gut: a novel treatment modality. The Journal of antimicrobial chemotherapy . 2003, 51,(2), 361-365.