Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
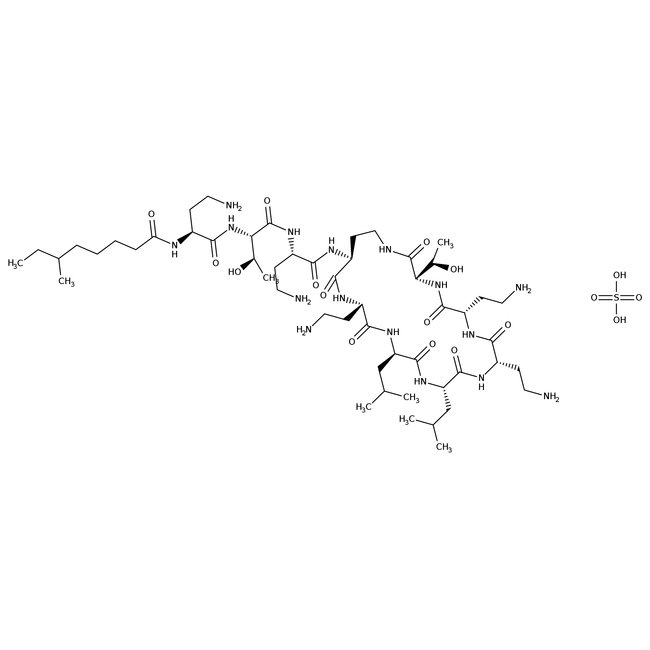
Colistin sulfate
| Catalog Number | Quantity |
|---|---|
| ALFJ60915.03 | 1 g |
Colistin sulfate A Polymyxin potent antibiotic and apoptosis inducer. This compound induces apoptosis through interaction with the cytoplasmic membrane. Colistin is a key microbiological component in Colistin Oxolinic Acid Blood Agar utilized in the cultivation of Aminobacter aminovorans, Bacillus species, Hyphomicrobium species and Methylobacterium species. It is also a critical component is VCN Inhibitor & VCNT Inhibitor growth media used in the isolation of Neisseria species.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
General Description
- Colistin Sulfate salt is a stable, cationic, water-soluble, white powder composed of over 30 components
- Originally isolated from B. polymyxa, it inhibits the growth of the Gram-negative (e.g. E. coli, P. aeruginosa, P. fluorescens, and S. enterica), and Gram-positive bacteria (e.g. L. lactis, P. polymyxa, P. acidilactici, and S. aureus) by permeabilizing the bacterial cell membrane
Applications
- Colistin Sulfate has potent anti-endotoxin activity rendered through its ability to bind lippopolysaccharides that make up bacterial endotoxins
- This compound is often used in the management of multi-drug resistant Gram-negative infections
General References:
- ME Falagas.; SK Kasiakou. Colistin: the revival of polymyxins for the management of multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacterial infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2005, 40 ,(9), 1333-1341.
- BP Kelleher.; KG Walshe.; JM Scott. Microbiological assay for vitamin B12 with use of a colistin-sulfate-resistant organism. Clinical Chemistry. 1987, 33 ,(1), 52-54.
- Falagas, M. E.; Kasiakou, S. K.; Saravolatz, L. D. Colistin: The Revival of Polymyxins for the Management of Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2005, 40 (9), 1333–1341.
- Suzuki, T.; Inouye, H.; Fujikawa, K.; et al. Studies on the chemical structure of colistin. I. Fractionation, molecular weight determination, amino acid and fatty acid composition. J. Biochem. 1963, 54(1), 25-33.
- Naghmouchi, K.; Hammami, R.; Fliss, I.; et al. Colistin A and colistin B among inhibitory substances of Paenibacillus polymyxa JB05-01-1. Arch. Microbiol. 2012, 194(5), 363-370.
- Mitsugui, C.S.; Tognim, M.C.B.; Cardoso, C.L.; et al. In vitro activity of polymyxins in combination with β-lactams against clinical strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Antimicrob. 2011, 38(5), 447-450.