Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
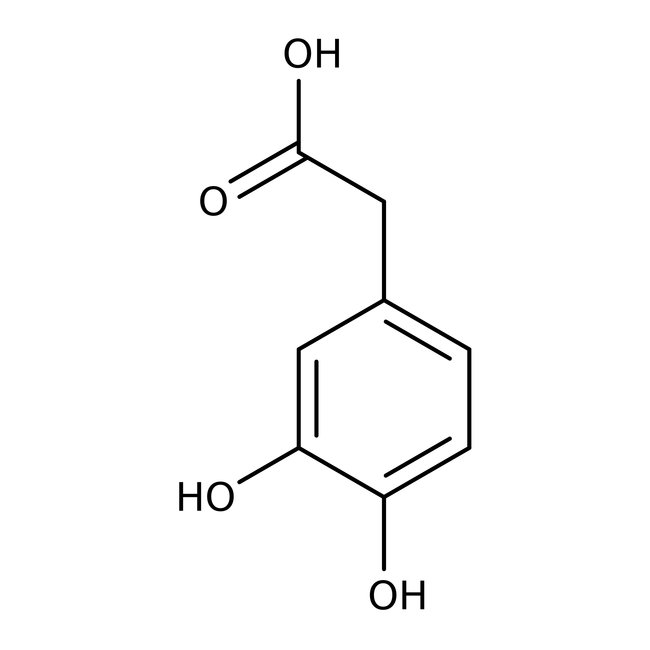
3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, 98+%
CAS: 102-32-9 | C8H8O4 | 168.148 g/mol
| Catalog Number | Quantity |
|---|---|
| ALFA15893.06 | 5 g |
Catalog number ALFA15893.06
View Price:Sign InSign in to see your account pricing. Need an account? Register with us today.
Quantity:
5 g
Specifications
Chemical Name or Material3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid
CAS102-32-9
Health Hazard 1H315-H319-H335
Health Hazard 2GHS H Statement
H315-H319-H335
Causes skin irritation.
Causes serious eye irritation.
May cause respiratory irritation.
H315-H319-H335
Causes skin irritation.
Causes serious eye irritation.
May cause respiratory irritation.
Health Hazard 3P261-P264b-P271-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P312-P332+P313-P362-P501c
View more
3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid is an important metabolite when studying the behavior of the dopaminergic system.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
Applications
3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid is an important metabolite when studying the behavior of the dopaminergic system.
Solubility
Soluble in water and methanol.
Notes
Store in cool place. Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place. Store under inert gas. Air sensitive. Incompatible with strong bases and strong oxidizing agents. Store at room temperature
3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid is an important metabolite when studying the behavior of the dopaminergic system.
Solubility
Soluble in water and methanol.
Notes
Store in cool place. Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place. Store under inert gas. Air sensitive. Incompatible with strong bases and strong oxidizing agents. Store at room temperature
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- Ariel Y. Deutch.; See-Ying Tam.; Robert H. Roth. Footshock and conditioned stress increase 3, 4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) in the ventral tegmental area but not substantia nigra. Brain Research. 1985, 333 (1), 143-146.
- Nicholas G. Bacopoulos.; Susan E. Hattox.; Robert H. Roth. 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and homovanillic acid in rat plasma: Possible indicators of central dopaminergic activity. European Journal of Pharmacology. 1979, 56 (3), 225-236.