Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
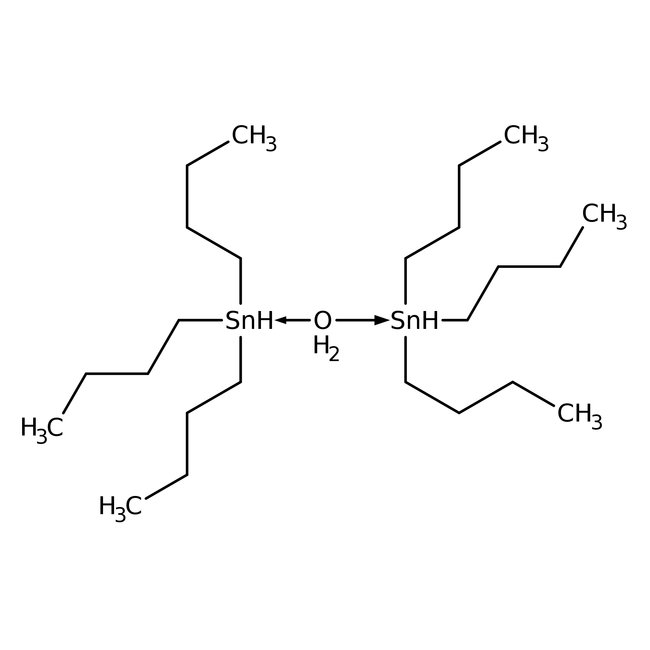
Bis(tri-n-butyltin) oxide, 97%
CAS: 56-35-9 | C24H58OSn2 | 600.15 g/mol
Catalog number ALFA13242.36
View Price:Sign InSign in to see your account pricing. Need an account? Register with us today.
Quantity:
500 g
Specifications
Chemical Name or MaterialBis(tri-n-butyltin) oxide
CAS56-35-9
Health Hazard 1H301-H312-H315-H319-H335-H360FD-H372
Health Hazard 2GHS H Statement
H301-H311-H360-H372-H315-H319
Toxic if swallowed.
Toxic in contact with skin.
May damage fertility or the unborn child.
Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure.
Causes skin irritation.
Causes serious eye irritation.
H301-H311-H360-H372-H315-H319
Toxic if swallowed.
Toxic in contact with skin.
May damage fertility or the unborn child.
Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure.
Causes skin irritation.
Causes serious eye irritation.
Health Hazard 3P201-P202-P260-P264b-P270-P271-P280i-P281-P301+P310-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P308+P313-P312-P330-P332+P313-P362-P501c
View more
Bis(tri-n-butyltin) oxide is employed in the synthesis of α,β-unsaturated methyl ketones, isoxazoles.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
Applications
Bis(tri-n-butyltin) oxide is employed in the synthesis of α,β-unsaturated methyl ketones, isoxazoles.
Solubility
Soluble in water (0.071 g/L)
Notes
Store at room temperature. Incompatible with oxidizing agents. Ensure adequate ventilation.
Bis(tri-n-butyltin) oxide is employed in the synthesis of α,β-unsaturated methyl ketones, isoxazoles.
Solubility
Soluble in water (0.071 g/L)
Notes
Store at room temperature. Incompatible with oxidizing agents. Ensure adequate ventilation.
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- E.I. Krajnc.; P.W. Wester.;J.G. Loeber.; F.X.R. van Leeuwen.; J.G. Vos.; H.A.M.G. Vaessen.; C.A. van der Heijden. Toxicity of bis(tri-n-butyltin)oxide in the rat: I. Short-term effects on general parameters and on the endocrine and lymphoid systems. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1984, 75 (3),363-386 .
- J.G. Vos.; A.De Klerk.; E.I. Krajnc.; H.Van Loveren.; J. Rozing. Immunotoxicity of Bis(tri-n-butyltin)oxide in the rat: Effects on thymus-dependent immunity and on nonspecific resistance following long-term exposure in young versus aged rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1990, 105 (1),144-155 .
- Reacts with alcohols to give tri-n-butylstannyl ethers which, for simple alcohols, are very susceptible to hydrolysis: Synthesis, 56 (1969); J. Organomet. Chem., 110, C57 (1976). In combination with bromine or NBS, allylic, benzylic and secondary alcohols are oxidized to carbonyl compounds, enabling the selective oxidation of secondary, in the presence of primary, alcohols: Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 49, 1656 (1976); Tetrahedron Lett., 4597 (1976); J. Am. Chem. Soc., 98, 1629 (1976). Similarly, sulfides give sulfoxides with no over-oxidation to sulfones: Tetrahedron Lett., 2413 (1977).
- Reacts with terminal alkynes to give alkynyl tin reagents. Where these reagents have electron-withdrawing substituents, they undergo regioselective cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes: Tetrahedron, 45, 1145 (1989):
- Converts thioamides to nitriles, as does Di-n-butyl tin oxide, L14491: J .Org. Chem., 47, 4594 (1982).
- Reagent for mild, selective non-hydrolytic deprotection of esters: Tetrahedron Lett., 32, 4239 (1991); J. Org. Chem., 59, 7259 (1994); Tetrahedron Lett., 36, 3311 (1995).