Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
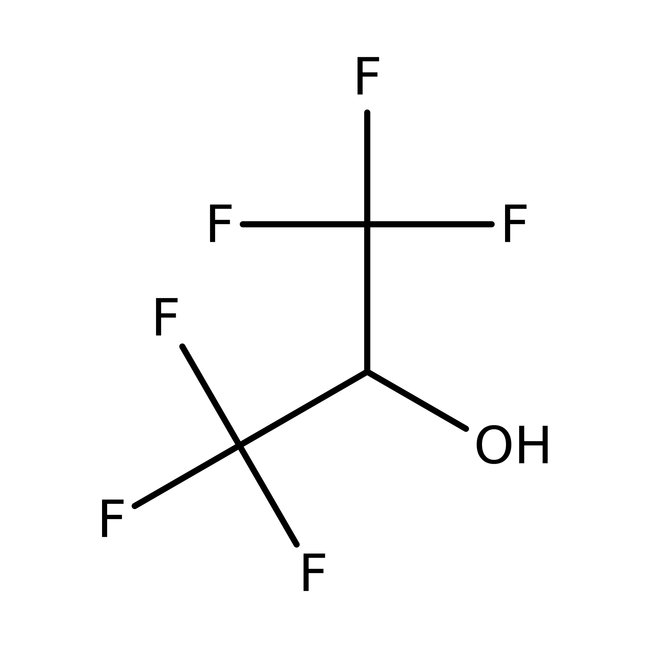
1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoro-2-propanol, 99+%
CAS: 920-66-1 | C3H2F6O | 168.038 g/mol
| Catalog Number | Quantity |
|---|---|
| ALFA12747.14 | 25 g |
Catalog number ALFA12747.14
View Price:Sign InSign in to see your account pricing. Need an account? Register with us today.
Quantity:
25 g
Specifications
Chemical Name or Material1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoro-2-propanol
CAS920-66-1
Health Hazard 1H302+H312+H332-H314-H335
Health Hazard 2GHS H Statement
H314-H318-H302-H332
Causes severe skin burns and eye damage.
Causes serious eye damage.
Harmful if swallowed.
Harmful if inhaled.
H314-H318-H302-H332
Causes severe skin burns and eye damage.
Causes serious eye damage.
Harmful if swallowed.
Harmful if inhaled.
Health Hazard 3P260-P264b-P270-P271-P280-P303+P361+P353-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P310-P330-P331-P363-P501c
View more
1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoro-2-propanol is used for preparing hexafluoroalcohol-functionalized methacrylate polymers for lithographic/nanopatterning materials. It plays an important role in the Friedel-Crafts reactions due to its polarity and high ionizing power. It finds use in sample preparation for GCMS. It also catalyzes the epoxidation of cyclooctene and 1-octene with hydrogen peroxide. It is used as a solvent for many reactions and to dissolve peptides. It is also employed to produce high-end chemicals like fluorinated surfactants, fluorinated emulsifier and fluorinated medicine. It acts as a cleaner in electronic industry.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
Applications
1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoro-2-propanol is used for preparing hexafluoroalcohol-functionalized methacrylate polymers for lithographic/nanopatterning materials. It plays an important role in the Friedel-Crafts reactions due to its polarity and high ionizing power. It finds use in sample preparation for GCMS. It also catalyzes the epoxidation of cyclooctene and 1-octene with hydrogen peroxide. It is used as a solvent for many reactions and to dissolve peptides. It is also employed to produce high-end chemicals like fluorinated surfactants, fluorinated emulsifier and fluorinated medicine. It acts as a cleaner in electronic industry.
Solubility
Miscible with water, chloroform, ether and acetone.
Notes
Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids, strong bases, aluminum, zinc and alkali metals.
1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoro-2-propanol is used for preparing hexafluoroalcohol-functionalized methacrylate polymers for lithographic/nanopatterning materials. It plays an important role in the Friedel-Crafts reactions due to its polarity and high ionizing power. It finds use in sample preparation for GCMS. It also catalyzes the epoxidation of cyclooctene and 1-octene with hydrogen peroxide. It is used as a solvent for many reactions and to dissolve peptides. It is also employed to produce high-end chemicals like fluorinated surfactants, fluorinated emulsifier and fluorinated medicine. It acts as a cleaner in electronic industry.
Solubility
Miscible with water, chloroform, ether and acetone.
Notes
Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids, strong bases, aluminum, zinc and alkali metals.
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- Valuable solvent of high polarity and low nucleophilicity: Tetrahedron Lett., 2335 (1974). Extremely powerful H bond donor but poor H bond acceptor: anions are highly solvated, but cations poorly. For feature article on the use of this unique solvent in the stabilization of radical cations, with particular application to EPR spectroscopy, see: Chem. Commun., 2105 (1996). Preferred solvent for the direct substitution of phenol ethers promoted by [Bis(trifluoroacetoxy) iodo]benzene, L15141: Tetrahedron Lett., 32, 4321 (1991). The intermediacy of radical cations in this reaction has been demonstrated: J. Am. Chem. Soc., 116, 3684 (1994). See also: J. Org. Chem., 60, 7144 (1995).
- Powerful solvent for oligopeptides: Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 61, 281 (1984); 66, 494 (1993). Used alone as a peptide coupling medium, HFIP gives poor results, but as a cosolvent along with proton acceptors such as DMF, good results, with improved peptide solubility, can be obtained: Tetrahedron Lett., 33, 7007 (1992).
- Effective solvent for uncatalyzed epoxidations of alkenes with H2O2 (caution! 60%): Synlett, 248 (2001); or, more conveniently, Urea hydrogen peroxide adduct, L13940: Eur. J. Org. Chem., 3290 (2002). Superior reaction medium for epoxidations, catalyzed by Hexafluoroacetone trihydrate, L10777: Synlett, 1305 (2001). An efficient, selective oxidation of sulfides to sulfoxides with 30% H2O2 employs HFIP as solvent, avoiding over-oxidation to the sulfone: Tetrahedron Lett., 39, 3141 (1998). For a review of fluorinated alcohols as solvents for selective and clean reactions, see: Synlett, 18 (2004).