Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
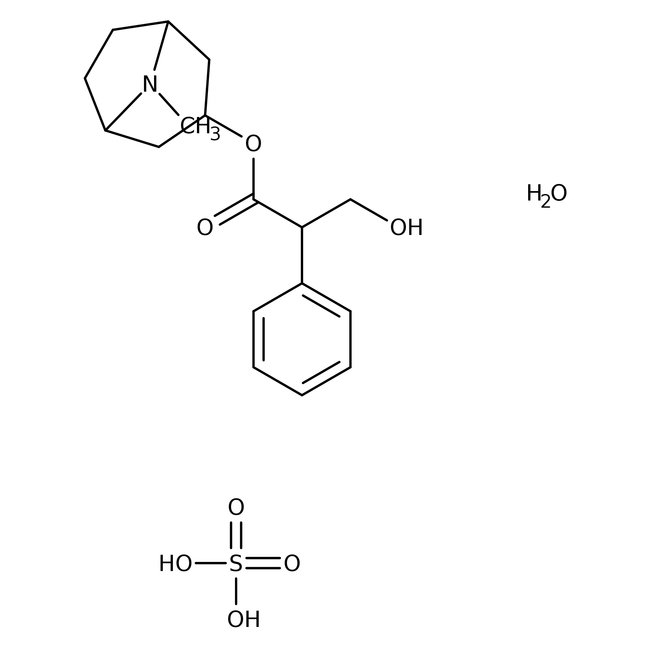
Atropine sulfate monohydrate, 97+%
Atropine sulfate monohydrate, CAS # 5908-99-6, is a muscarinic receptor antagonist. | CAS: 5908-99-6 | H2SO4·H2O | 694.85 g/mol
Catalog number FSA226681000
Price (MYR)
3,641.00
EA
Quantity:
100 g
Packaging:
Glass bottle
Price (MYR)
3,641.00
EA
Specifications
Chemical Name or MaterialAtropine sulfate monohydrate
AcidityPasses Test
CAS5908-99-6
Health Hazard 1GHS Signal Word: Danger
Health Hazard 2GHS H Statement:
May cause respiratory irritation.
Fatal if swallowed.
Causes skin irritation.
Fatal if inhaled.
May cause an allergic skin reaction.
Causes serious eye irritation.
May cause respiratory irritation.
Fatal if swallowed.
Causes skin irritation.
Fatal if inhaled.
May cause an allergic skin reaction.
Causes serious eye irritation.
View more
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Acros Organics product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Acros Organics product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
General Description
- Atropine is a competitive and reversible antagonist of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors on both central and peripheral neurons
- Atropine was originally isolated from the belladonna plant Atropa belladonna but is also found in other Solanaceae plants
- Atropine is a drug that can be used to slow heart rate, decrease salivary secretions, and treat poisoning caused by cholinergic or muscarinic agents
Applications
- It is used to block activation of muscarinic receptors in laboratory mice
- It can be used in a laboratory setting to decrease oral and airway secretions in research animals
- Atropine has been used to study heart rate and blood pressure variability in swine
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- Driessen, A.K.; McGovern, A.E.; Behrens, R.; Moe, A.A.K.; Farrell, M.J.; Mazzone, S.B. A role for neurokinin 1 receptor expressing neurons in the paratrigeminal nucleus in bradykinin-evoked cough in guinea-pigs. J Physiol. 2020, 598(11), 2257-2275.
- Egorov, A.V.; Schumacher, D.; Medert, R., Birnbaumer, L.; Freichel, M.; Draguhn, A. TRPC channels are not required for graded persistent activity in entorhinal cortex neurons. Hippocampus. 2019 Nov;29(11):1038-1048. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23094.
- Poletto, R.; Janczak, A.M.; Marchant-Forde, R.M.; Marchant-Forde, J.N.; Matthews, D.L.; Dowell, C.A.; Hogan, D.F.; Freeman, L.J.; Lay, D.C. Jr. Identification of low and high frequency ranges for heart rate variability and blood pressure variability analyses using pharmacological autonomic blockade with atropine and propranolol in swine. Physiol Behav. 2011 May 3;103(2):188-96.