Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
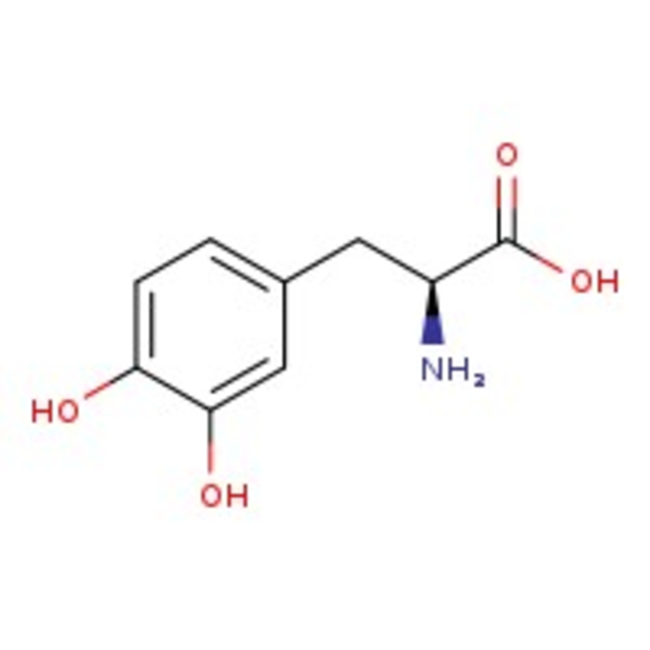
3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine, 99%
3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine (levodopa orL-dopa), CAS # 59-92-7, is a dopamine precursor molecule. | CAS: 59-92-7 | C9H11NO4 | 197.19 g/mol
Catalog number FSA167531000
View Price:Sign InSign in to see your account pricing. Need an account? Register with us today.
Quantity:
100 g
Packaging:
Glass Bottle
Specifications
Chemical Name or Material3-(3, 4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine
CAS59-92-7
Health Hazard 1Warning
Health Hazard 2GHS H Statement:
Harmful if swallowed.
Harmful if swallowed.
Health Hazard 3GHS P Statement:
IF SWALLOWED: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician if you feel unwell.
WARNING: The information provided on this web site was developed in compliance with European Union (EU) regulations and is correct to the best of our knowledge, information and belief at the date of its publication. The information given is designed only as a guide for safe handling and use. It is not to be considered as either a warranty or quality specification.
IF SWALLOWED: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician if you feel unwell.
WARNING: The information provided on this web site was developed in compliance with European Union (EU) regulations and is correct to the best of our knowledge, information and belief at the date of its publication. The information given is designed only as a guide for safe handling and use. It is not to be considered as either a warranty or quality specification.
View more
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Acros Organics product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Acros Organics product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
General Description
• 3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine, or L-dopa, is converted to dopamine by DOPA decarboxylase in the body
• Upon conversion to dopamine, it acts as an excitatory neurotransmitter
Applications
• L-dopa is useful in the laboratory study of Parkinson’s to replenish dopamine in depleted circuits
• L-dopa has also been used for laboratory research on hypertension and melanocyte activity
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- Maini Rekdal, V.; Bess, E.N.; Bisanz, J.E.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Balskus EP. Discovery and inhibition of an interspecies gut bacterial pathway for Levodopa metabolism. Science. 2019, 364(6445), eaau6323.
- Hong, C.T.; Chan, L.; Bai, C.H. The Effect of Caffeine on the Risk and Progression of Parkinson's Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2020, 12(6), 1860.