Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
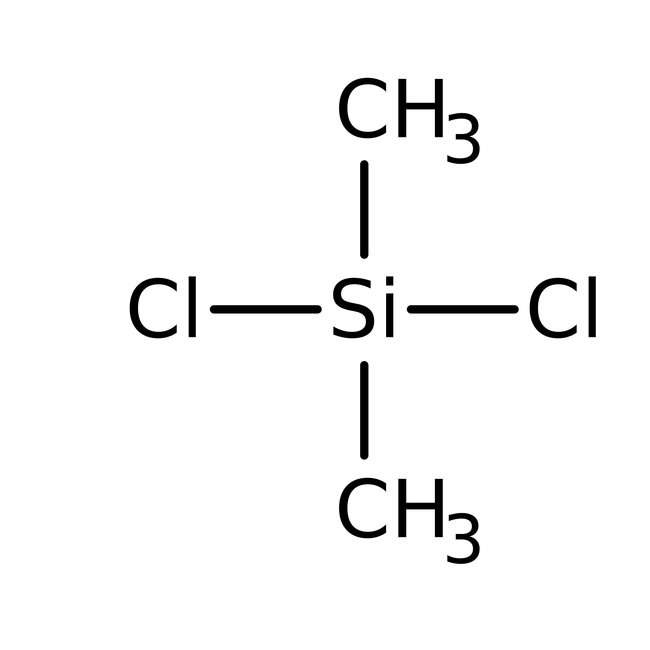
Dichlorodimethylsilane, 98+%
CAS: 75-78-5 | C2H6Cl2Si | 129.055 g/mol
Catalog number ALFL12133.36
View Price:Sign InSign in to see your account pricing. Need an account? Register with us today.
Quantity:
500 g
Specifications
Boiling Point70°C to 71°C
Chemical Name or MaterialDichlorodimethylsilane
Melting Point∼-76°C
CAS75-78-5
Health Hazard 1H225-H302-H314-H331-H335
View more
Dichlorodimethylsilane is used to prepare a resin bound siloxane with tertiary alcohols and it is also used as a reagent for synthesis of optically active ansa-mettallocene polymerization catalysts. It acts as a precursor to silicone and polysilane compounds. It is also used in the glass coating to protect it from micro particles. It is involved in the preparation of resin bound siloxane with reactivity towards tertiary alcohols.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
Applications
Dichlorodimethylsilane is used to prepare a resin bound siloxane with tertiary alcohols and it is also used as a reagent for synthesis of optically active ansa-mettallocene polymerization catalysts. It acts as a precursor to silicone and polysilane compounds. It is also used in the glass coating to protect it from micro particles. It is involved in the preparation of resin bound siloxane with reactivity towards tertiary alcohols.
Solubility
Immiscible with water.
Notes
Moisture sensitive. Store in a cool place. Incompatible with alcohols, amines and strong bases.
Dichlorodimethylsilane is used to prepare a resin bound siloxane with tertiary alcohols and it is also used as a reagent for synthesis of optically active ansa-mettallocene polymerization catalysts. It acts as a precursor to silicone and polysilane compounds. It is also used in the glass coating to protect it from micro particles. It is involved in the preparation of resin bound siloxane with reactivity towards tertiary alcohols.
Solubility
Immiscible with water.
Notes
Moisture sensitive. Store in a cool place. Incompatible with alcohols, amines and strong bases.
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- Silicone intermediate and silylating agent, forming dimethylsilylene derivatives of diols. The main limitation of these is their extreme susceptibilty to hydrolysis. See Appendix 4.
- For use in combination with triflic acid to generate dimethyldisilyl triflate, and its use in synthesis, see N,N'-Diacetyl hydrazine, A13393 .
- Kim, Y. R.; Lai, S. C. S.; McKelvey, K.; Zhang, G.; Perry, D.; Miller, T. S.; Unwin, P. R. Nucleation and aggregative growth of palladium nanoparticles on carbon electrodes: experiment and kinetic model. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119 (30), 17389-17397.
- Wang, Z.; Gong, X.; Ngai, T. Measurements of Long-Range Interactions between Protein-Functionalized Surfaces by Total Internal Reflection Microscopy. Langmuir. 2015, 31 (10), 3101-3107.