Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
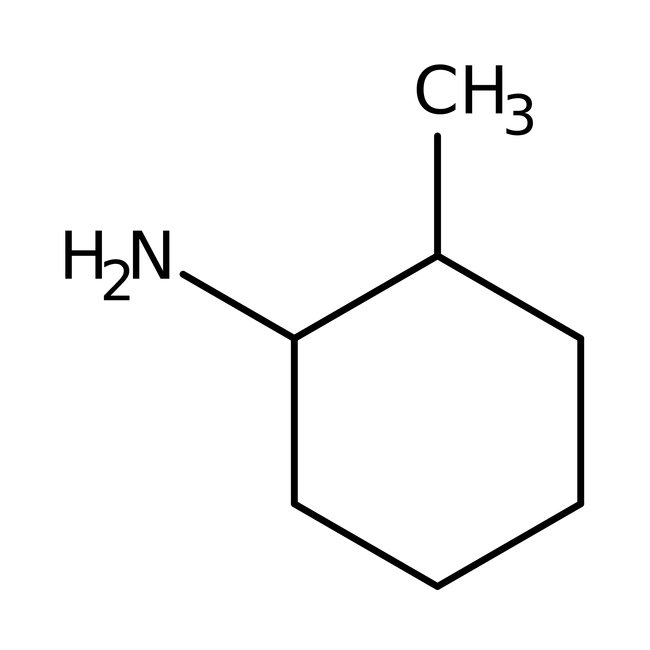
2-Methylcyclohexylamine, cis + trans, 97%
CAS: 7003-32-9 | C7H15N | 113.20 g/mol
Catalog number ALFL02285.18
View Price:Sign InSign in to see your account pricing. Need an account? Register with us today.
Quantity:
50 g
Specifications
Chemical Name or Material2-Methylcyclohexylamine
Name NoteCis + Trans
CAS7003-32-9
Health Hazard 1H225-H302+H312+H332-H314
Health Hazard 2GHS H Statement
H225-H314-H318
Highly flammable liquid and vapor.
Causes severe skin burns and eye damage.
Causes serious eye damage.
H225-H314-H318
Highly flammable liquid and vapor.
Causes severe skin burns and eye damage.
Causes serious eye damage.
View more
2-Methylcyclohexylamine is an important raw material and intermediate used in organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals and dyestuff fields.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
Applications
2-Methylcyclohexylamine is an important raw material and intermediate used in organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals and dyestuff fields.
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water.
Notes
Keep container tightly sealed. Store in cool, dry conditions in well sealed containers. Incompatible with oxidizing agents. Store under dry inert gas. It is sensitive to air.
2-Methylcyclohexylamine is an important raw material and intermediate used in organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals and dyestuff fields.
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water.
Notes
Keep container tightly sealed. Store in cool, dry conditions in well sealed containers. Incompatible with oxidizing agents. Store under dry inert gas. It is sensitive to air.
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- Michael W. Rathke.; Naoto Inoue.; K. R. Varma.; Herbert C. Brown. A Stereospecific Synthesis of Alicyclic and Bicyclic Amines via Hydroboration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1966, 88 (12), 2870-2871.
- Rota F.; Prins R. Mechanism of the C-N-bond breaking in the hydrodenitrogenation of methylcyclohexylamine over sulfided NiMo/γ-Al2O3. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2000, 162(1), 367-74.