Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
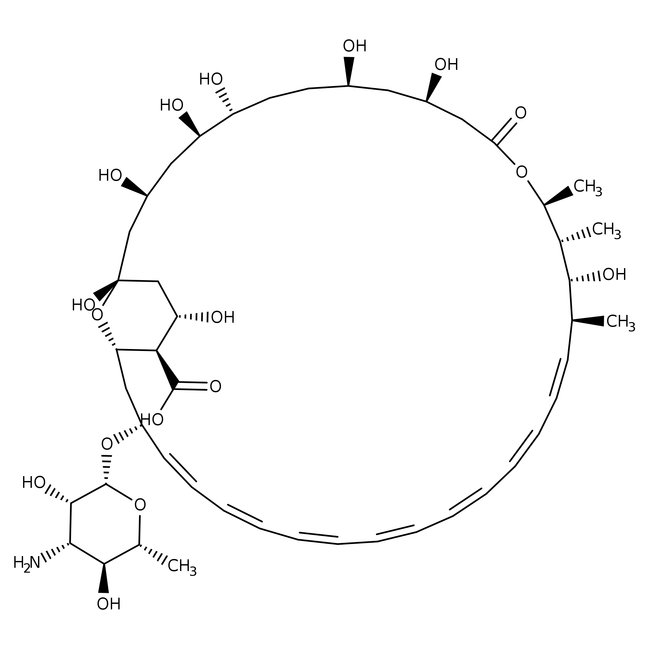
Amphotericin B, Streptomyces nodosus
Amphotericin B, CAS # 1397-89-3, is an antifungal that has been used against fungus caused by protozoan parasites of Leishmania genus. | CAS: 1397-89-3 | C47H73NO17 | 924.09 g/mol
Catalog number ALFJ61491.MC
Price (MYR)
544.00
EA
Quantity:
100 mg
Price (MYR)
544.00
EA
Specifications
Chemical Name or MaterialAmphotericin B
TypeAmphotericin B
Name NoteStreptomyces nodosus
Physical FormPowder
CAS1397-89-3
View more
Amphotericin B, antifungal activity has been used against leishmaniasis caused by protozoan parasites of the Leishmania genus. Amphotericin B trihydrate was observed to cause suppression of bone marrow progenitor cells and to induce Actinomycin D(CR001) sensitivity in drug resistant HELA cells in vitro.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
General Description
- Amphotericin B is an antibiotic that has antifungal activity and is produced mainly by Streptomyces nodosus
Applications
- It has antifungal activity against fungus caused by protozoan parasites of Leishmania genus by binding to an essential component of the fungal cell membrane and altering cell membrane permeability
- It can suppress bone marrow progenitor cells and induce Actinomycin D(CR001) sensitivity in drug resistant HELA cells in vitro
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- Boulware, R.D. et. al. Timing of antiretroviral therapy after diagnosis of cryptococcal meningitis. New England Journal of Medicine. 2014, 370, (26), 2487-2498.
- Sarkar, S. et. al. Therapeutic activation of macrophages and microglia to suppress brain tumor-initiating cells. Nature Neuroscience. 2014, 17, (1), 46-55.