Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
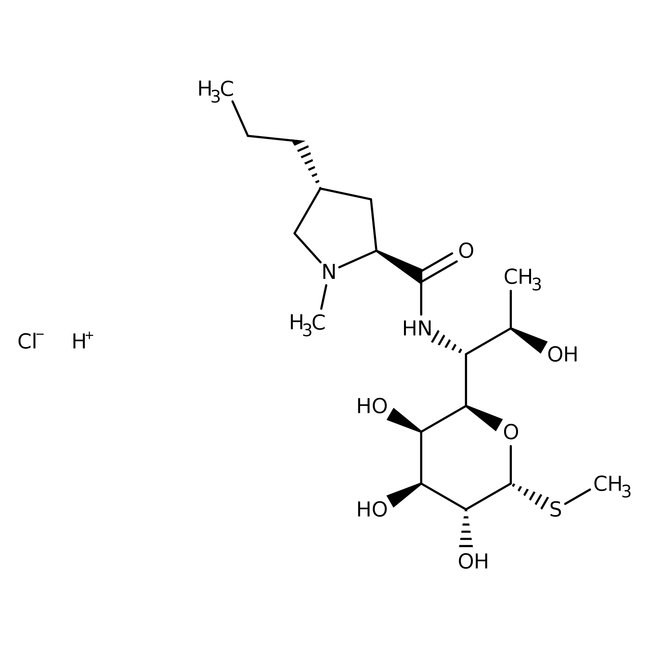
Lincomycin hydrochloride
Lincomycin hydrochloride, CAS # 859-18-7, is a compound showing antibacterial activity against a wide variety of bacteria, including Staphylococcal, Streptococcal, and Bacteroides fragilis infections. It also shows inhibitory activity against protein synthesis. | CAS: 859-18-7 | C18H35ClN2O6S | 442.996 g/mol
| Catalog Number | Quantity |
|---|---|
| ALFJ61251.03 | 1 g |
Catalog number ALFJ61251.03
View Price:Sign InSign in to see your account pricing. Need an account? Register with us today.
Quantity:
1 g
Specifications
Chemical Name or MaterialLincomycin hydrochloride
TypeLincomycin Hydrochloride
Physical FormCrystalline Powder
CAS859-18-7
Health Hazard 1H315-H319-H335
View more
Lincomycin hydrochloride is used to study the inhibition of protein synthesis, bacterial antibiotic resistance and protein and surfactant binding. It has been used in the treatment of Staphylococcal, Streptococcal, and Bacterioides fragilis infections.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
General Description
- Lincomycin hydrochloride is a lincosamide compound with antibacterial activity originally identified in the actinomycete, Streptomyces lincolnensis, with activity against gram-positive cocci and anaerobic bacteria
- Lincomycin inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by forming cross-links within the peptidyl transferase loop region of the 23S rRNA
Application
- Lincomycin hydrochloride is commonly used to study the inhibition of protein synthesis, bacterial antibiotic resistance, and protein and surfactant binding
- It has been used against Staphylococcal, Streptococcal, and Bacteroides fragilis species
- It is protective against the development of mastitis in a mouse model of acute mastitis induced by S. aureus
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- Neelam Keswani; Sinjan Choudhary; Nand Kishore. Interaction of weakly bound antibiotics neomycin and lincomycin with bovine and human serum albumin: biophysical approach. Journal of Biochemistry. 2010, 148,(1), 71-84.
- H.Malke; W.Reichardt; M.Hartmann; F.Walter. Genetic study of plasmid-associated zonal resistance to lincomycin in Streptococcus pyogenes. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 1981, 19,(1), 91-100.
- Yancey, R.J., Jr.; Kinney, M.L., and Ford, C.W. Efficacy of lincosaminide antibiotics in the treatment of experimental staphylococcal mastitis in lactating mice. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1985, 15, (2), 219-232.
- Neelam Keswani; Sinjan Choudhary; Nand Kishore. Interaction of weakly bound antibiotics neomycin and lincomycin with bovine and human serum albumin: biophysical approach. Journal of Biochemistry. 2010, 148 (1), 71-84.
- H.Malke; W.Reichardt; M.Hartmann; F.Walter. Genetic study of plasmid-associated zonal resistance to lincomycin in Streptococcus pyogenes. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 1981, 19 (1), 91-100.