Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
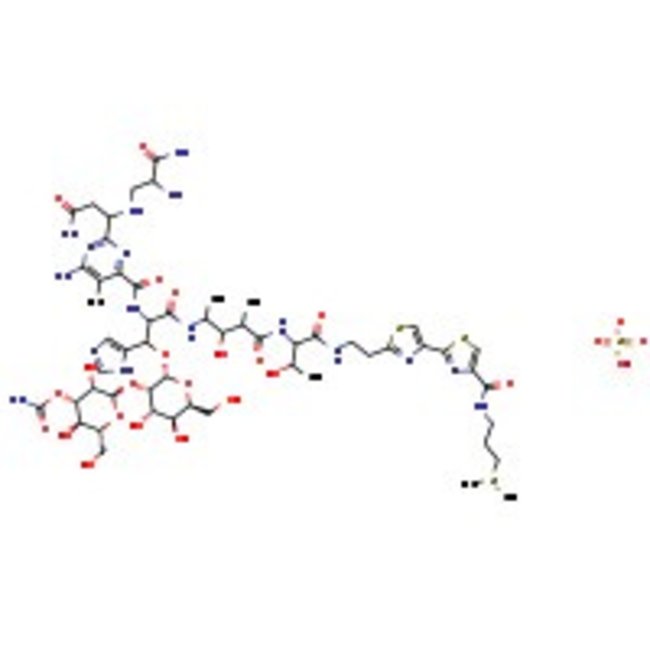
Bleomycin sulfate
Bleomycin sulfate, CAS # 9041-93-4, is a glycopeptide compound with antibiotic activity isolated from Streptomyces verticillus. It also exhibits anticancer activity. | CAS: 9041-93-4 | C55H85N17O25S4 | 1512.619 g/mol
| Catalog Number | Quantity |
|---|---|
| ALFJ60727.MA | 10 mg |
Catalog number ALFJ60727.MA
View Price:Sign InSign in to see your account pricing. Need an account? Register with us today.
Quantity:
10 mg
Specifications
Chemical Name or MaterialBleomycin sulfate
TypeBleomycin Sulfate
Physical FormPowder
CAS9041-93-4
Health Hazard 1H340-H351-H361d
View more
Bleomycin sulfate is used as a glycopeptide antibiotic. It is capable of inducing oxidative cleavage of the DNA backbone, leading to apoptosis and also degrades RNA, and has been reported to display selectivity for RNA over DNA. Bleomycin acts as a sclerosing agent.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
General Description
- Bleomycin sulfate was initially isolated from Streptomyces verticillus. It is a glycopeptide compound with antibiotic activity
- It has the ability to induce oxidative cleavage of the DNA backbone, leading to apoptosis
- Bleomycin sulfate can form a complex with iron that reduces oxygen to superoxide and hydroxyl radicals. These reactive oxygen species can cause single- and double-stranded breaks in DNA as well as promote carbohydrate oxidation, lipid peroxidation, and alterations in prostaglandin synthesis and degradation
Application
- It can be used to inhibit DNA metabolism and slow or stop cell growth. This property explains its anticancer activity
- Bleomycin sulfate can also be used to degrade RNA as it is more selective to RNA than DNA
- Local injections of bleomycin sulfate in mouse models can induce sclerotic skin mimicking scleroderma
- In laboratory research, bleomycin is used to induce pulmonary fibrosis in mice
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- WB Shelley.; ED Shelley. Intralesional bleomycin sulfate therapy for warts: a novel bifurcated needle puncture technique. Arch Dermatol. 1991, 127,(2), 234-236.
- M Amer.; N Diab.; A Ramadan.; A Galal. Therapeutic evaluation for intralesional injection of bleomycin sulfate in 143 resistant warts. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 2015, 73,(4), 533-720.