Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
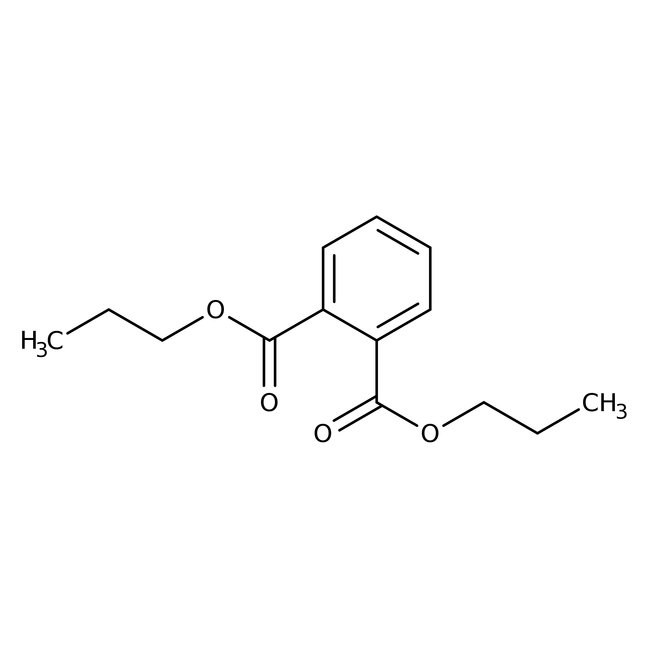
Di-n-propyl phthalate, 98%
CAS: 131-16-8 | C14H18O4 | 250.294 g/mol
| Catalog Number | Quantity |
|---|---|
| ALFB24056.09 | 10 g |
Catalog number ALFB24056.09
View Price:Sign InSign in to see your account pricing. Need an account? Register with us today.
Quantity:
10 g
Specifications
Chemical Name or MaterialDi-n-propyl phthalate
CAS131-16-8
Health Hazard 1Warning
Health Hazard 2GHS H Statement
H361
Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child.
H361
Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child.
Health Hazard 3GHS P Statement
P281-P201-P202-P308+P313-P405-P501a
Use personal protective equipment as required.
Obtain special instructions before use.
Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
Store locked up.
Dispose of contents/container in accordance with local/regional/national/international regulations.
P281-P201-P202-P308+P313-P405-P501a
Use personal protective equipment as required.
Obtain special instructions before use.
Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
Store locked up.
Dispose of contents/container in accordance with local/regional/national/international regulations.
View more
Di-n-propyl phthalate is used to make plasticizers and polymer additives. It is also used in chemical reagents, organic intermediates.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
Applications
Di-n-propyl phthalate is used to make plasticizers and polymer additives. It is also used in chemical reagents, organic intermediates.
Solubility
Soluble in chloroform, methanol.
Notes
Store in a cool, dry place in tightly closed container. Store at room temperature. Incompatible with oxidizing agents.
Di-n-propyl phthalate is used to make plasticizers and polymer additives. It is also used in chemical reagents, organic intermediates.
Solubility
Soluble in chloroform, methanol.
Notes
Store in a cool, dry place in tightly closed container. Store at room temperature. Incompatible with oxidizing agents.
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- Yang-Hoon Kim; Jiho Min; Kyung-Dong Bae; Man Bock Gu; Jeewon Lee. Biodegradation of dipropyl phthalate and toxicity of its degradation products: a comparison of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. pisi cutinase and Candida cylindracea esterase. Archives of Microbiology. 2005, 184 (1), 25-31.
- Y Imai, A Kondo; H Iizuka; T Maruyama; K Kurohane. Effects of phthalate esters on the sensitization phase of contact hypersensitivity induced by fluorescein isothiocyanate. Clinical and Experimental Allergy. 2006, 36 (11), 1462-1468.