Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
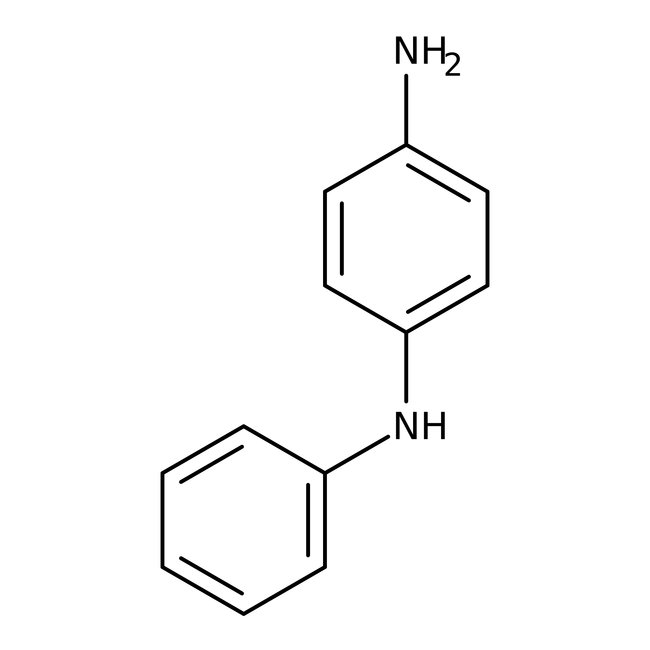
N-Phenyl-p-phenylenediamine, 98%
CAS: 101-54-2 | C12H12N2 | 184.242 g/mol
| Catalog Number | Quantity |
|---|---|
| ALFB23867.22 | 100 g |
Catalog number ALFB23867.22
View Price:Sign InSign in to see your account pricing. Need an account? Register with us today.
Quantity:
100 g
Specifications
Chemical Name or MaterialN-Phenyl-p-phenylenediamine
CAS101-54-2
Health Hazard 1H302+H332-H315-H317-H319-H335
Health Hazard 2GHS H Statement
H301-H315-H319-H317-H335
Toxic if swallowed.
Causes skin irritation.
Causes serious eye irritation.
May cause an allergic skin reaction.
May cause respiratory irritation.
H301-H315-H319-H317-H335
Toxic if swallowed.
Causes skin irritation.
Causes serious eye irritation.
May cause an allergic skin reaction.
May cause respiratory irritation.
Health Hazard 3P261-P264b-P270-P271-P272-P280-P301+P312-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P312-P330-P333+P313-P362-P501c
View more
p-Anilinoaniline is an antioxidant that has shown to cause a reduction of NOx emissions from soybean biodiesel powered DI diesel engines but has increased CO and HC emissions. It is also used to produce dyes, pharmaceuticals, and photographic chemicals and frmerly used as a hair dye.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
Applications
p-Anilinoaniline is an antioxidant that has shown to cause a reduction of NOx emissions from soybean biodiesel powered DI diesel engines but has increased CO and HC emissions. It is also used to produce dyes, pharmaceuticals, and photographic chemicals and frmerly used as a hair dye.
Solubility
Soluble in water at 20°C 0.6g/L. Soluble in (10 mg/mL) ethanol.
Notes
Store away from oxidizing agents. Keep the container tightly closed and place it in a cool, dry and well ventilated condition.
p-Anilinoaniline is an antioxidant that has shown to cause a reduction of NOx emissions from soybean biodiesel powered DI diesel engines but has increased CO and HC emissions. It is also used to produce dyes, pharmaceuticals, and photographic chemicals and frmerly used as a hair dye.
Solubility
Soluble in water at 20°C 0.6g/L. Soluble in (10 mg/mL) ethanol.
Notes
Store away from oxidizing agents. Keep the container tightly closed and place it in a cool, dry and well ventilated condition.
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- W. Pearl, et al. Microdetermination Of Cytochrome Oxidase In Rat Tissues By The Oxidation Of N-Phenyl-P-Phenylenediamine Or Ascorbic Acid. Histochem Cytochem.,1963,11(1), 102-107.
- R. L. Dryer, et al. The determination of phosphorus and phosphatase with N-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine.The Journal of Biological Chemistry,1957,225177-184.