Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
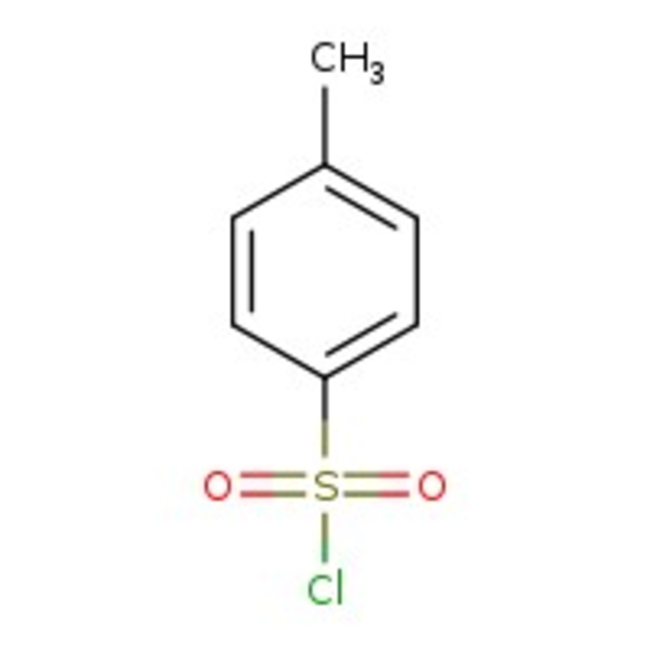
p-Toluenesulfonyl chloride, 98%
CAS: 98-59-9 | C7H7ClO2S | 190.64 g/mol
Catalog number ALFA14547.36
Price (MYR)
455.00
EA
Quantity:
500 g
Price (MYR)
455.00
EA
Specifications
Chemical Name or Materialp-Toluenesulfonyl chloride
CAS98-59-9
Health Hazard 1H290-H315-H317-H318
Health Hazard 2GHS H Statement
H314-H318
Causes severe skin burns and eye damage.
Causes serious eye damage.
H314-H318
Causes severe skin burns and eye damage.
Causes serious eye damage.
Health Hazard 3P234-P261-P264b-P272-P280-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338-P310-P333+P313-P362-P390-P501c
View more
p-Toluenesulfonyl chloride is used as a precursor in the production of dyes and saccharin. It acts as a dehydrating agent in the conversion of urea to carbodiimide and converts alcohols into the corresponding toluenesulfonate esters. It is also employed as a flow-promoting agent for paints, an adhesive, nitrocellulose, coating material and as a plasticizer for polyamides. Furthermore, it serves as an antistatic agent, as a gloss enhancer in plastic film preparations and as a basic material of electroplating solutions.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
Applications
p-Toluenesulfonyl chloride is used as a precursor in the production of dyes and saccharin. It acts as a dehydrating agent in the conversion of urea to carbodiimide and converts alcohols into the corresponding toluenesulfonate esters. It is also employed as a flow-promoting agent for paints, an adhesive, nitrocellulose, coating material and as a plasticizer for polyamides. Furthermore, it serves as an antistatic agent, as a gloss enhancer in plastic film preparations and as a basic material of electroplating solutions.
Solubility
Soluble in alcohol, benzene and ether. Insoluble in water.
Notes
Moisture sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and strong bases.
p-Toluenesulfonyl chloride is used as a precursor in the production of dyes and saccharin. It acts as a dehydrating agent in the conversion of urea to carbodiimide and converts alcohols into the corresponding toluenesulfonate esters. It is also employed as a flow-promoting agent for paints, an adhesive, nitrocellulose, coating material and as a plasticizer for polyamides. Furthermore, it serves as an antistatic agent, as a gloss enhancer in plastic film preparations and as a basic material of electroplating solutions.
Solubility
Soluble in alcohol, benzene and ether. Insoluble in water.
Notes
Moisture sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and strong bases.
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- For a detailed study of the optimum conditions for the tosylation of primary and secondary alcohols in pyridine, see: J. Org. Chem., 51, 2386 (1986). For use of 1,4-Diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane, A14003, as an alternative to pyridine in the tosylation of alcohols, see: Synthesis, 1433 (1997). In the presence of a carboxylic acid, the ester is formed in high yield: J. Am. Chem. Soc., 77, 6214 (1955); 79, 2146 (1957). Esterification of an unprotected amino acid can be effected by heating the tosylate salt with tosyl chloride in an alcohol solvent: J. Org. Chem., 48, 121 (1983).
- In the presence of strong bases, 1,2-diols can be converted to epoxides: Synthesis, 706 (1977); 983 (1985); Synth. Commun., 23, 285 (1993), and 1,3-diols to oxetanes: Synthesis, 550 (1981).
- N-Tosylation has been used to block the imidazole nucleus in histidine: Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 42, 1466 (1969); 47, 3146 (1974), and arginine residues: Experientia, 24, 661 (1968), during peptide synthesis. Cleavage can be effected with HF. See Appendix 6.
- Dehydrating agent, e.g. for conversion of ureas to carbodiimides: Org. Synth. Coll., 5, 555 (1973); Synthesis, 520 (1987).
- Cooley, T. A.; Riley, S.; Biros, S. M.; Staples, R. J.; Ngassa, F. N. Crystal structure of 2, 4-dinitrophenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate: a new polymorph. Nano lett. 2015, 71 (9), 1085-1088.
- Jiang, X.; Yu, G. W.; Li, Z. G.; Chu, S. P.; Wang, S. P. Synthesis and characterisation of phosphazene derivatives containing dioxybiphenyl and 4-sulfanylquinazoline groups. J. Chem. Res., Synop. 2015, 39 (3), 162-165.