Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
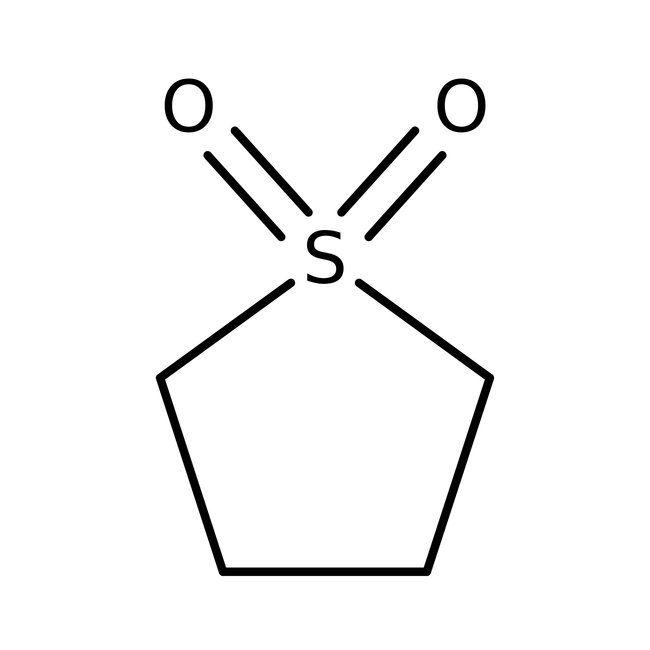
Sulfolane, 99%
Miscible with water, acetone, toluene | CAS: 126-33-0 | C4H8O2S | 120.17 g/mol
Catalog number ALFA13466.30
View Price:Sign InSign in to see your account pricing. Need an account? Register with us today.
Quantity:
250 g
Specifications
Chemical Name or MaterialSulfolane
CAS126-33-0
Health Hazard 1H302
Health Hazard 2GHS H Statement
H302
Harmful if swallowed.
H302
Harmful if swallowed.
Health Hazard 3P264b-P270-P301+P312-P330-P501c
View more
Sulfolane is used as an industrial solvent utilized for the extraction of aromatic hydrocarbons from hydrocarbon mixtures and to purify natural gas. Further, it is used in refineries and the petrochemical industry.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
Applications
Sulfolane is used as an industrial solvent utilized for the extraction of aromatic hydrocarbons from hydrocarbon mixtures and to purify natural gas. Further, it is used in refineries and the petrochemical industry.
Solubility
Miscible with alcohol, water, acetone, toluene and dilute mineral acids. Slightly miscible with octanes, olefins and naphthenes.
Notes
Miscible with water, acetone, tolueneIncompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
Sulfolane is used as an industrial solvent utilized for the extraction of aromatic hydrocarbons from hydrocarbon mixtures and to purify natural gas. Further, it is used in refineries and the petrochemical industry.
Solubility
Miscible with alcohol, water, acetone, toluene and dilute mineral acids. Slightly miscible with octanes, olefins and naphthenes.
Notes
Miscible with water, acetone, tolueneIncompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- High-boiling dipolar aprotic solvent. Compare Dimethyl sulfoxide, A13280, N,N-Dimethyl acetamide, A10924 and 1-Methyl-2-pyrrolidinone, A12260.
- Solvent for nitrations using Nitronium tetrafluoroborate, B20167.
- Widely used as solvent in the nucleophilic displacement of chloroaromatics with F- (Halex fluorination). For example, chlorinated benzaldehydes were converted to their fluoro-analogues by heating with KF in tetramethylene sulfone at 220°: J. Fluorine Chem., 46, 529 (1990). Nitro groups have also been displaced by F- by heating in the presence of tetramethylammonium chloride and phthaloyl chloride as a nitrite trap: J. Org. Chem., 56, 6406 (1991). See, however, Tetrahydrothiophene 1-oxide, A17502 and Potassium fluoride, 14130.
- Use of this solvent makes possible the reduction of alkyl bromides to alkanes by NaBH4: Tetrahedron Lett., 3495 (1969).
- Can be doubly metallated at the ɑ-positions with strong bases such as NaNH2, LiNH2 or n-BuLi, and the resulting dianion reacted with one or two equivalents of benzophenone to give the mono- or bis-adduct respectively: J. Org. Chem., 35, 1834 (1970); J. Organomet. Chem., 59, 53 (1973). For alkylation of the monolithio-derivative, see: Synth. Commun., 18, 583 (1988).
- Solvent for the Baylis-Hillman reaction, using 1,4-Diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane, A14003, which enables short reaction times at room temperature: Tetrahedron Lett., 45, 1183 (2004).
- Vergaelen, M.; Verbraeken, B.; Monnery, B. D.; Hoogenboom, R. Sulfolane as Common Rate Accelerating Solvent for the Cationic Ring-Opening Polymerization of 2-Oxazolines. ACS Macro Lett. 2015, 4 (8), 825-828.
- Raghuram, N.; Suresh, R.; Ramesh, G.; Sowjanya, G.; Jyostna, T. S. Excess parameters for the binary mixtures of sulfolane with chloroethanes at different temperatures. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 119 (3), 2107-2117.