Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
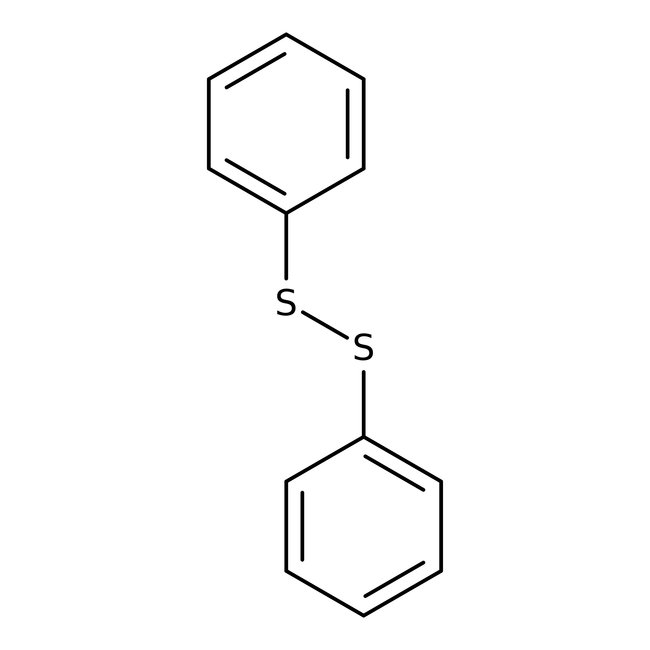
Diphenyl disulfide, 98%
CAS: 882-33-7 | C12H10S2 | 218.332 g/mol
Catalog number ALFA12586.30
View Price:Sign InSign in to see your account pricing. Need an account? Register with us today.
Quantity:
250 g
Specifications
Chemical Name or MaterialDiphenyl disulfide
CAS882-33-7
Health Hazard 1H315-H319-H335
Health Hazard 2GHS H Statement
H315-H319-H335
Causes skin irritation.
Causes serious eye irritation.
May cause respiratory irritation.
H315-H319-H335
Causes skin irritation.
Causes serious eye irritation.
May cause respiratory irritation.
Health Hazard 3P261-P264b-P271-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P312-P332+P313-P362-P501c
View more
Diphenyl disulfide is one of the most popular organic disulfides used in organic synthesis. It is used as a reagent for the α-phenylsulfenylation of carbonyl compounds. It participates in hydrothiolation of alkynes via amine-mediated single electron transfer mechanism. It is the hydrolysis product of dyfonate.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
Applications
Diphenyl disulfide is one of the most popular organic disulfides used in organic synthesis. It is used as a reagent for the α-phenylsulfenylation of carbonyl compounds. It participates in hydrothiolation of alkynes via amine-mediated single electron transfer mechanism. It is the hydrolysis product of dyfonate.
Solubility
Insoluble in water.
Notes
Stable under recommended storage conditions. Incompatible with oxidizing agents.
Diphenyl disulfide is one of the most popular organic disulfides used in organic synthesis. It is used as a reagent for the α-phenylsulfenylation of carbonyl compounds. It participates in hydrothiolation of alkynes via amine-mediated single electron transfer mechanism. It is the hydrolysis product of dyfonate.
Solubility
Insoluble in water.
Notes
Stable under recommended storage conditions. Incompatible with oxidizing agents.
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- Tsuyoshi Taniguchi; Tatsuya Fujii; Atsushi Idota; Hiroyuki Ishibashi. Reductive addition of the benzenethiyl radical to alkynes by amine-mediated single electron transfer reaction to diphenyl disulfide. Organic Letters. 2009, 11, (15)3298-3301
- S.C.Mitchell; R.M.Nickson; E.R.Porter; W.F.Jackson; S.L.Preston; A.Q.Zhang. The fate of diphenyl sulphide, diphenyl sulphoxide and diphenyl sulphone in the rat. Drug Metabolism and Drug Interactions. 2000, 16, (3)191-206
- Sulfenylation agent for enolates of ketones, esters or carboxylic acid dianions: J. Am. Chem. Soc., 95, 6840 (1973); 98, 4887 (1976); Chem. Rev., 78, 363 (1978). Oxidation to the sulfoxide and thermal elimination can be used for the conversion of ketones to enones via thermal sulfoxide elimination, less frequently used than the selenoxide route (cf preceding entry), due to the higher temperatures required.
- Also sulfenylates organolithium reagents from, e.g. lithiated furans: J. Org. Chem., 46, 2473 (1981).
- Alkyl halides under phase-transfer conditions give alkyl phenyl sulfides in good yields,: Synth. Commun., 12, 595 (1982), and alkenyl halides in the presence of CuI give alkenyl sulfides: Chem. Lett., 769 (1989).
- For use as a catalyst in the photochemical cis-trans isomerization of olefins (used in the synthesis of the macrolide ricinelaidic acid lactone), see: Org. Synth. Coll., 7, 470 (1990).