Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
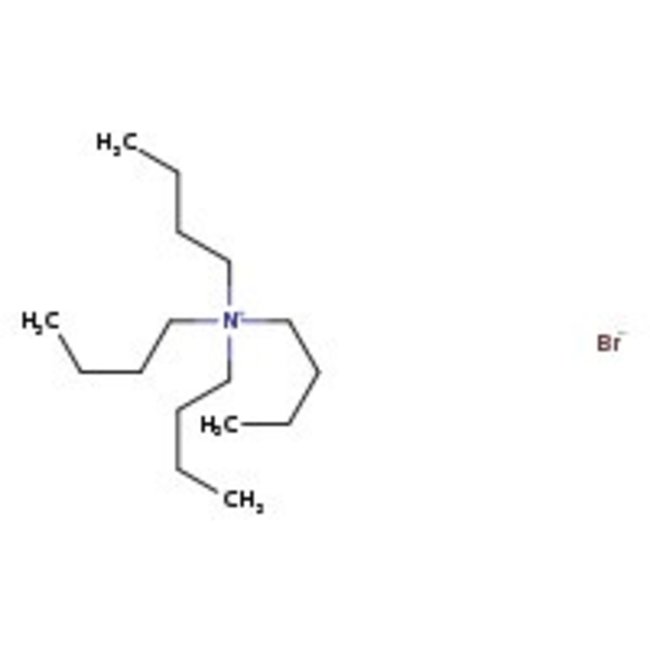
Tetra-n-butylammonium bromide, 98+%
CAS: 1643-19-2 | C16H36BrN | 322.375 g/mol
Catalog number ALFA10249.36
Price (MYR)
1,535.00
EA
Quantity:
500 g
Price (MYR)
1,535.00
EA
Specifications
Chemical Name or MaterialTetra-n-butylammonium bromide
CAS1643-19-2
Health Hazard 1H315-H319-H335
Health Hazard 2GHS H Statement
H315-H319-H335
Causes skin irritation.
Causes serious eye irritation.
May cause respiratory irritation.
H315-H319-H335
Causes skin irritation.
Causes serious eye irritation.
May cause respiratory irritation.
Health Hazard 3P261-P264b-P271-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P312-P332+P313-P362-P501c
View more
Phase transfer catalyst Tetra-n-butylammonium bromide is used as a phase transfer catalyst for the preparation of lactones by cyclization of potassium salt of μ-bromocarboxylic acids and beta-lactones from beta-bromoacid by cyclization. It is also involved in the Curtius rearrangement, N-alkylation of aromatic carboxamides. It plays an important role as an ionic liquid in the regioselective O-alkylation reactions. It is also used in the preparation of polymer solar cells and single component green-light emitting electrochemical cells.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
Applications
Phase transfer catalyst Tetra-n-butylammonium bromide is used as a phase transfer catalyst for the preparation of lactones by cyclization of potassium salt of µ-bromocarboxylic acids and beta-lactones from beta-bromoacid by cyclization. It is also involved in the Curtius rearrangement, N-alkylation of aromatic carboxamides. It plays an important role as an ionic liquid in the regioselective O-alkylation reactions. It is also used in the preparation of polymer solar cells and single component green-light emitting electrochemical cells.
Solubility
Soluble in water and ethanol.
Notes
Hygroscopic. Keep the container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
Phase transfer catalyst Tetra-n-butylammonium bromide is used as a phase transfer catalyst for the preparation of lactones by cyclization of potassium salt of µ-bromocarboxylic acids and beta-lactones from beta-bromoacid by cyclization. It is also involved in the Curtius rearrangement, N-alkylation of aromatic carboxamides. It plays an important role as an ionic liquid in the regioselective O-alkylation reactions. It is also used in the preparation of polymer solar cells and single component green-light emitting electrochemical cells.
Solubility
Soluble in water and ethanol.
Notes
Hygroscopic. Keep the container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- Phase-transfer catalyst of wide application. Some illustrative examples are given below. See also Appendix 2.
- K salts of ω-bromocarboxylic acids can be cyclized to lactones under effectively high-dilution conditions by extracting into toluene in the presence of a small amount of catalyst. The 16-membered ring lactone was formed in 92% yield: J. Org. Chem., 48, 1533 (1983).
- Primary alkyl chlorides can be converted to alcohols in excellent yield by phase-transfer reaction with sodium formate and hydrolysis of the resulting formate esters: Synthesis, 763 (1986).
- ß-Lactones are formed by the cyclization of ß-bromoacids under phase-transfer conditions: Chem. Pharm. Bull., 29, 1063 (1981).
- An improved procedure for the Curtius rearrangement involves reaction of acid chlorides with azide ion under phase-transfer conditions: Synthesis, 38 (1983).
- Aromatic carboxamides undergo N-alkylation with alkyl halides using KOH under solvent-free conditions: Synth. Commun., 22, 1661 (1992).
- Has been used as an ionic liquid in the regioselective O-alkylation of ambident nucleophiles: Tetrahedron Lett., 33, 4435 (1992). A method is described whereby the solvent can be recovered quantitatively. A semi-molten mixture with KF or CsF has been found to be an effective system for fluorodehalogenation of, e.g., benzyl bromide: J. Fluorine Chem., 73, 185 (1995).
- Effective catalyst for amination reactions of alkyl or activated aryl halides, by increasing the solubility of ammonia in organic media: J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 267 (1987).